In the realm of manufacturing, the importance of effective process control cannot be overstated. Process control serves as a critical framework that ensures product quality, consistency, and efficiency while minimizing waste and operational costs. As industries face increasing pressure to optimize production lines and respond swiftly to market demands, implementing robust process control strategies becomes essential for achieving competitive advantage.
In this guide, we will explore ten essential tips that will empower manufacturers to enhance their process control systems. Each tip will focus on specific aspects of process management, from leveraging technology to fostering a culture of continuous improvement. By adopting these practices, organizations can streamline operations, reduce variability, and ultimately deliver superior products that meet or exceed customer expectations. Whether you are a seasoned professional or new to the field, understanding these key elements of process control will enable you to drive operational excellence in your manufacturing processes.

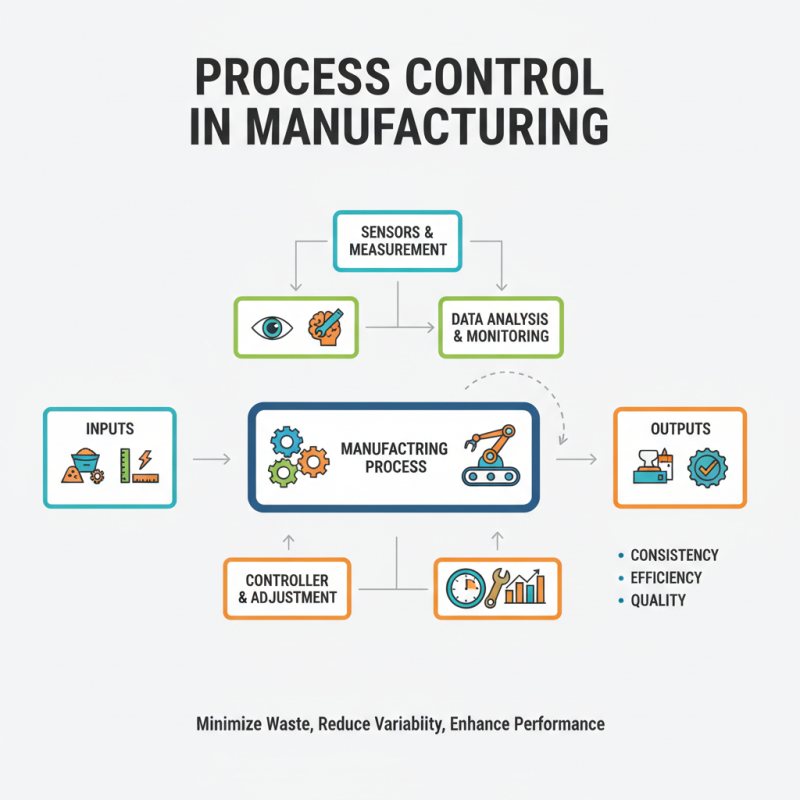
Process control in manufacturing is a systematic approach that aims to maintain the desired output of a manufacturing process by monitoring and adjusting various parameters. Understanding the fundamentals of process control is crucial for achieving consistency, efficiency, and quality in production. It involves the use of various control methods, such as feedback loops and automatic adjustments, to respond to fluctuations in conditions that may affect the production process. By grasping these concepts, manufacturers can design processes that minimize waste, reduce variability, and enhance overall performance.
One of the key components of effective process control is the establishment of clear metrics and objectives. By defining specific performance indicators, companies can track their progress and identify areas for improvement. Additionally, implementing advanced data analytics tools allows for real-time monitoring and analysis of processes, enabling quick response to any deviations from the set parameters. This proactive approach not only helps in maintaining product quality but also contributes to sustainable manufacturing practices, as it optimizes resource usage and reduces environmental impact. Understanding the interplay of these elements is essential for any manufacturer aiming to stay competitive in today’s fast-paced industry.
Identifying key performance indicators (KPIs) is crucial for effective monitoring in manufacturing process control. KPIs serve as quantifiable metrics that help managers assess the efficiency and quality of processes. By establishing clear, relevant KPIs, manufacturers can pinpoint areas for improvement, ensuring that production operates at optimal levels. Common KPIs include cycle time, defect rates, and overall equipment effectiveness (OEE). Each metric provides insights into specific aspects of the manufacturing process, allowing for targeted interventions and enhancements.
To leverage KPIs effectively, manufacturers should select indicators that align with their strategic goals and operational priorities. This alignment ensures that the metrics not only reflect current performance but also drive continuous improvement. Regularly reviewing and updating KPIs in response to changes in production demands or technology advancements is equally important. By fostering an adaptive approach to KPI management, organizations can maintain a competitive edge and promote a culture of accountability and performance excellence within their teams.
Automation technologies play a pivotal role in enhancing process control within the manufacturing sector. By implementing advanced automation solutions, manufacturers can achieve precise monitoring and management of production processes. This not only minimizes human error but also allows for real-time data collection and analysis, leading to quicker decision-making and more efficient operations. Automated systems can track key performance indicators (KPIs) and enable seamless integration across various stages of production, ensuring consistent product quality and optimal resource utilization.
Moreover, automation facilitates adaptive process control that can respond dynamically to varying conditions on the shop floor. For example, machine learning algorithms can analyze production data to identify patterns and predict potential issues before they occur. This predictive capability ensures that manufacturers can take proactive measures, reducing downtime and enhancing operational efficiency. Additionally, automation can streamline workflows by utilizing robotics and automated guided vehicles (AGVs), effectively optimizing material handling and reducing bottlenecks in the production line. Embracing such technologies not only strengthens overall process control but also positions manufacturers to meet the demands of an increasingly competitive landscape.
Implementing continuous improvement strategies in manufacturing is vital for enhancing process control and ensuring operational excellence. One effective approach is to embrace methodologies such as Lean, Six Sigma, or Kaizen, which focus on eliminating waste and improving efficiency. By systematically analyzing workflow and identifying bottlenecks, manufacturers can streamline processes, leading to reduced cycle times and increased productivity. Engaging employees in this effort fosters a culture of accountability and innovation, as they can provide valuable insights and take ownership of their work environments.
Moreover, fostering a mindset of continuous improvement requires regular training and development opportunities for staff. Providing employees with the tools and knowledge they need to identify areas for enhancement empowers them to contribute meaningfully to the organization’s goals. Additionally, utilizing data analytics can help manufacturers monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) and make informed decisions based on real-time insights. By continuously tracking progress and adjusting strategies as needed, companies can better adapt to changes in the market and maintain a competitive edge.
| Tip Number | Tip | Description | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Standardize Processes | Develop standardized operating procedures to ensure consistency. | Reduced variability and improved quality. |
| 2 | Use Data Analytics | Leverage data analytics tools to monitor process performance. | Informed decision-making and predictive maintenance. |
| 3 | Train Employees | Provide regular training to enhance skills and knowledge. | Increased employee engagement and productivity. |
| 4 | Implement KPIs | Set key performance indicators to measure process efficiency. | Clear performance tracking and accountability. |
| 5 | Continuous Feedback Loops | Create systems for ongoing feedback from employees and machines. | Immediate identification and resolution of issues. |
| 6 | Lean Manufacturing | Adopt lean principles to minimize waste and optimize flow. | Increased efficiency and cost savings. |
| 7 | Root Cause Analysis | Conduct root cause analysis for recurring issues. | Effective resolution and prevention of future problems. |
| 8 | Enhance Communication | Foster open communication pathways within teams. | Stronger collaboration and problem-solving capabilities. |
| 9 | Technology Integration | Integrate cutting-edge technologies for automating processes. | Enhanced precision and reduced manual error. |
| 10 | Evaluate and Refine | Regularly evaluate process performance and make necessary adjustments. | Sustained improvement and adaptability to changes. |
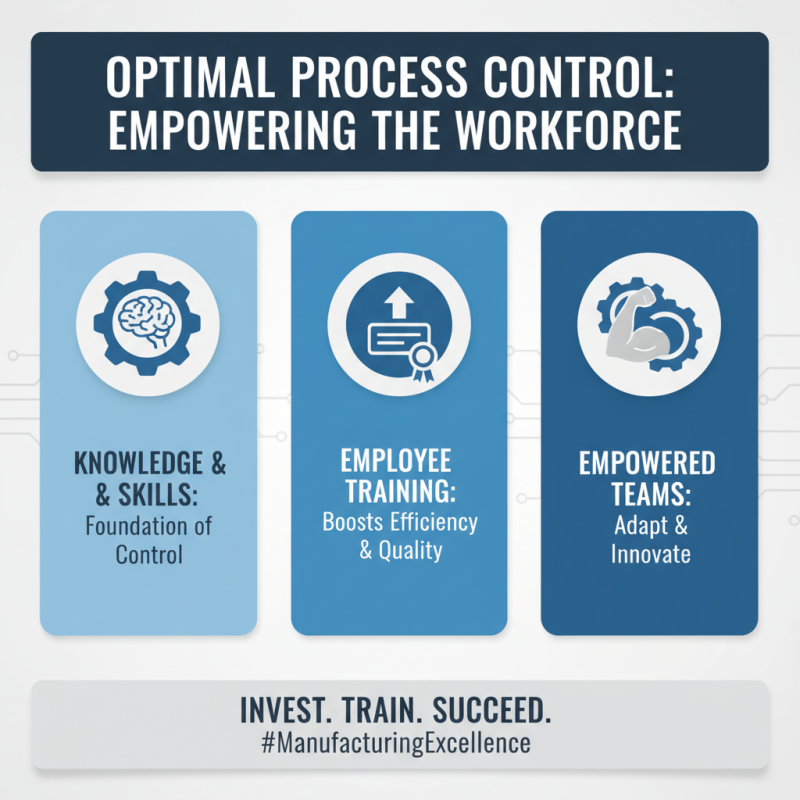
Effective process control in manufacturing relies heavily on the knowledge and skills of the workforce. Training employees in optimal process management techniques is essential for ensuring operational efficiency and product quality. By investing in employee training, organizations can empower their teams to recognize and adapt to production challenges, leading to a more streamlined process.
One critical tip for enhancing process control is to implement regular training sessions that focus on the latest technologies and methods in manufacturing. Such training not only keeps employees informed but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement. Encouraging open discussion during these sessions allows employees to share insights and experiences, thereby enriching the learning environment. Another important aspect is to provide hands-on training, where employees can apply the concepts learned in real-time scenarios. This practical approach solidifies their understanding and enhances their problem-solving skills.
Additionally, creating a mentoring program where experienced staff guide newer employees can significantly improve process management. This fosters collaboration and knowledge transfer, allowing for the sharing of best practices and innovation. By cultivating a work environment that values ongoing education and skill development, companies can achieve remarkable improvements in process control and operational excellence.






